
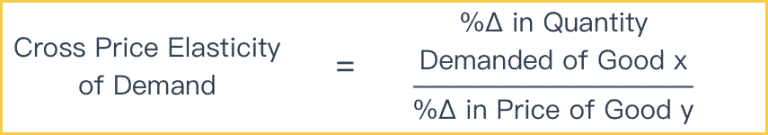
The full PED formula is 𝑷𝑬𝑫= 𝑸𝟐−𝑸𝟏 𝑸𝟏 ÷ 𝑷𝟐−𝑷𝟏 𝑷𝟏ġ.2 Elasticities PED Price Elasticity of Demand – definition and formula Notice from the previous slide that our PED was a negative value. PED Price Elasticity of Demand – definition and formula Price Elasticity of Demand (PED) is a measurement of how much the quantity demanded for a good will change as a result of a particular change in the good’s price. Price elasticity of Supply (PES): Measures the responsiveness of producers of a particular good to a change in the price of that good.ģ 1.2 Elasticities Price Elasticity of Demand – definition and formula Income Elasticity of Demand (YED): Measures the responsiveness of consumers of a particular good to a change in their income. Cross-price elasticity of Demand (XED): Measures the responsiveness of consumers of one good to a change in the price of a related goo (either a substitute or a complement). There are four types of elasticity that we will study in this unit: Price Elasticity of Demand (PED): Measures the responsiveness of consumers of a particular good to a change in the good’s price. Unit Overview Price Elasticity of Demand (PED) PED and its determinants The total revenue test of PED Applications of PED Cross Price Elasticity of Demand (XED) XED and its determinants Applications of XED Income Elasticity of Demand (YED) YED and its determinants Applications of YED Price Elasticity of Supply (PES) PES and its determinants Applications of PES Elasticities Online: Elasticity Substitutes Inferior goods Elasticities Video Lessons Practice ActivitiesĮlasticity is an economic concept which refers to the responsiveness among consumers or producers to a change in a variable which affects either the market demand or the market supply. Revenue rises when Ped <1 and a business raises their average selling price.1 1.2 Elasticities Price Elasticity of Demand (PED) If Ped = (-) 1.6 then ticket sales will rise by 1.6 x 12.5% = 20%Ī local council raises the price of car parking from £3 per day to £5 per day and finds that usage of car parks contracts from 1,200 cars a day to 900 cars per day.Ĭalculate the price elasticity of demand for this price change and calculate whether total revenue from the car park rises or falls. Ped = % change in Qty Demanded / % change in Price They estimate that the price elasticity of demand for tickets is (-) 1.6.Ĭalculate the expected number of tickets sold if they reduce the ticket price to £7.

Price Elasticity of Demand - Two Example CalculationsĪ cinema charges £8 per ticket for evening screenings and sells 250 tickets a night on average.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
